41 r factor levels labels
R Factors - Operating on Factors and Factor Levels - TechVidvan labels is an optional vector of labels for the levels in the factor, exclude is a set of values that are excluded from the levels of the factor, ordered is a logical value that determines whether the factor is an ordered or unordered factor, nmax is an upper limit on the number of levels. Code: Data Wrangling: De factores, levels and labels - R que R Vamos a crear un nuevo objeto especificando los levels y los labels para dejar claro la diferencia entre ambas: vab_pc_fct_levels_labels <- factor (vab_pc, levels = c ("muy.baja", "baja", "media", "alta", "muy.alta"), labels = c ("nivel_muy_bajo", "nivel_bajo", "nivel_medio", "nivel_alto", "nivel_muy_alto"))
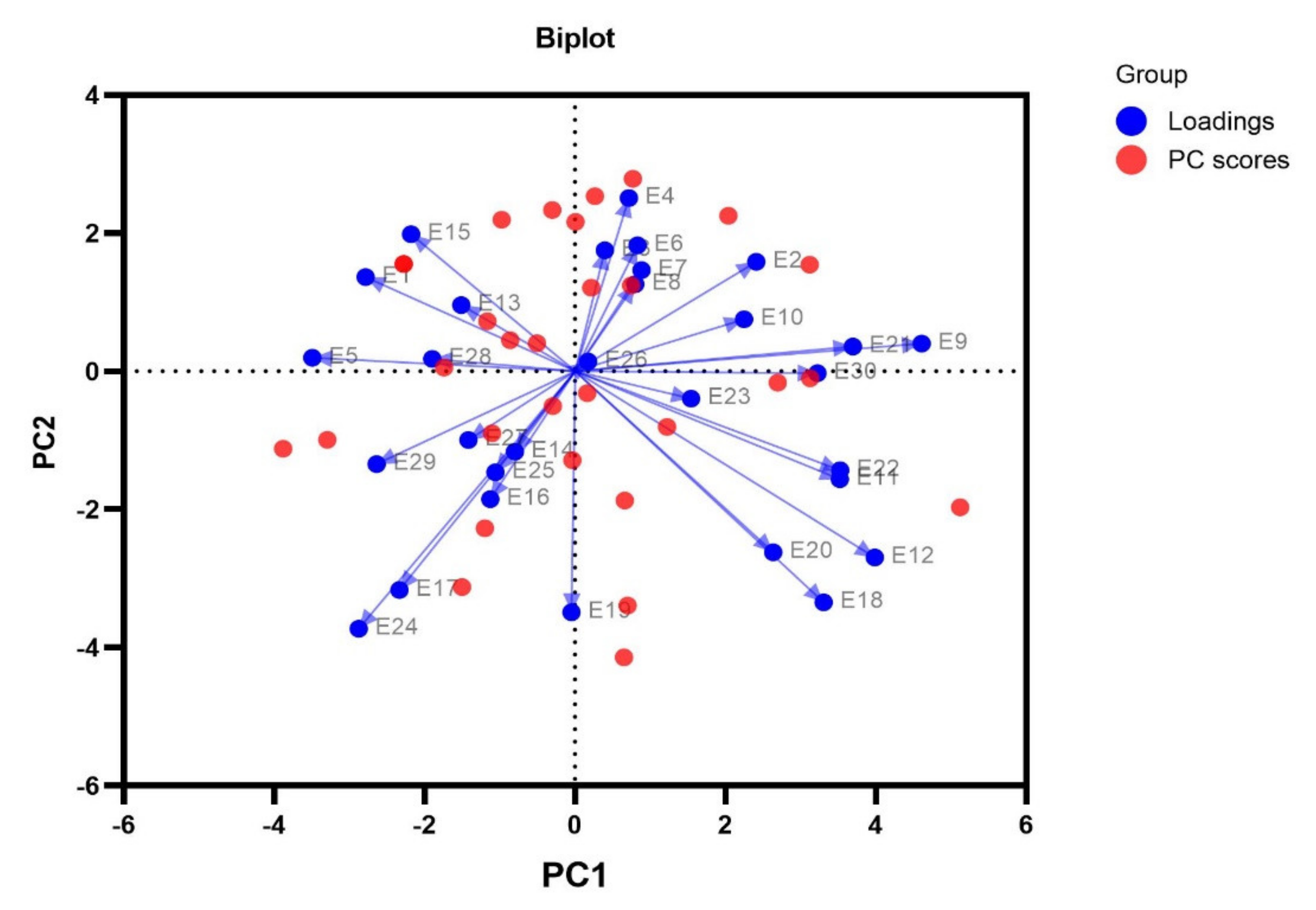
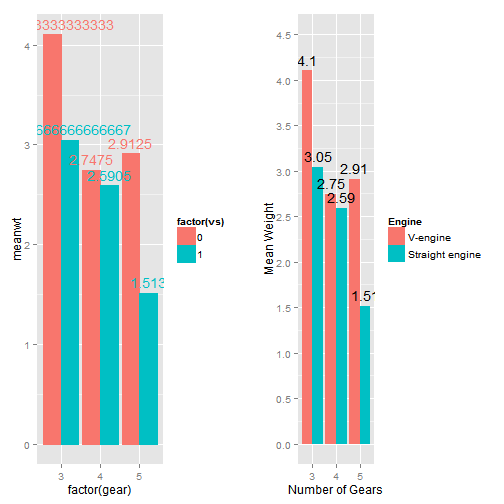
15.9 Changing the Order of Factor Levels Based on Data Values | R ... Figure 15.1: Original data (left); Reordered by the mean of each group (middle); Reordered by the median of each group (right) In the middle plot in Figure 15.1, the boxes are sorted by the mean. The horizontal line that runs across each box represents the median of the data. Notice that these values do not increase strictly from left to right.
R factor levels labels
gl() Function in R (2 Examples) | How to Generate Factor Levels & Labels As you can see based on the previous output of the RStudio console, we have created a new data object called x1, which contains 15 elements and three different factor levels. Example 2: Specify Labels within gl () Function The following R code illustrates how to change the values (i.e. the labels) of a factor variable created by the gl function. Factor variables | R Learning Modules Factor variables. Version info: Code for this page was tested in R version 3.0.2 (2013-09-25) On: 2013-11-27 With: knitr 1.5 1. Creating factor variables. Factor variables are categorical variables that can be either numeric or string variables. There are a number of advantages to converting categorical variables to factor variables. Getting Started with R - Part 7: Factors - Levels and Labels You can set the levels labels after constructing a factor. This would be similar to passing in the labels parameter. We can pass a full new vector or just labels the labels of the levels selectively. Let us just change factor label 1 from "Jack" to "Mr. Prelutsky". levels(repeat_factor_labeled) [1] <- "Mr. Prelutsky" repeat_factor_labeled
R factor levels labels. Change Legend Labels of ggplot2 Plot in R (2 Examples) In this post, I'll explain how to modify the text labels of a ggplot2 legend in R programming. The tutorial will consist of these content blocks: 1) Exemplifying Data, Add-On Packages & Basic Graphic. 2) Example 1: Change Legend Labels of ggplot2 Plot Using scale_color_manual Function. 3) Example 2: Rename Factor Levels to Change Legend ... R 因子 | 菜鸟教程 R 语言创建因子使用 factor () 函数,向量作为输入参数。 factor () 函数语法格式: factor(x = character(), levels, labels = levels, exclude = NA, ordered = is.ordered(x), nmax = NA) 参数说明: x:向量。 levels:指定各水平值, 不指定时由x的不同值来求得。 labels:水平的标签, 不指定时用各水平值的对应字符串。 exclude:排除的字符。 ordered:逻辑值,用于指定水平是否有序。 nmax:水平的上限数量。 以下实例把字符型向量转换成因子: 实例 x <- c("男", "女", "男", "男", "女") sex <- factor( x) R - Factors - GeeksforGeeks Oct 27, 2021 · Ordered: This logical attribute decides whether the levels are ordered. nmax: It will decide the upper limit for the maximum number of levels. Creating a Factor in R Programming Language. The command used to create or modify a factor in R language is – factor() with a vector as input. The two steps to creating a factor are: Creating a vector factor function - RDocumentation The function factor is used to encode a vector as a factor (the terms 'category' and 'enumerated type' are also used for factors). If argument ordered is TRUE , the factor levels are assumed to be ordered. For compatibility with S there is also a function ordered >. is.factor, is.ordered, as.factor and as.ordered are the ...
How to Change the Levels of a Factor in R - ProgrammingR We want to rename factor levels in r so they are easier to understand. Let's take look at their values: # look at factor levels in r for wool > levels (warpbreaks$wool) [1] "A" "B" # look at factor levels in r for tension > levels (warpbreaks$tension) [1] "L" "M" "H" How to Reorder Factor Levels in R (With Examples) - Statology How to Reorder Factor Levels in R (With Examples) Occasionally you may want to re-order the levels of some factor variable in R. Fortunately this is easy to do using the following syntax: factor_variable <- factor(factor_variable, levels=c ('this', 'that', 'those', ...)) The following example show how to use this function in practice. How to Rename Factor Levels in R (With Examples) - Statology How to Reorder Factor Levels in R. Published by Zach. View all posts by Zach Post navigation. Prev How to Calculate Cosine Similarity in Excel. Next How to Plot Multiple Histograms in R (With Examples) Leave a Reply Cancel reply. Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked * R Factor and Factor Levels: How to Create Factors in R - R-Lang Factors in R are the data objects used to categorize the data and store it as levels. Factors can store both strings and integers. Factors can be ordered or unordered and are an important class for statistical analysis and for plotting. Factors are saved as integers and have labels associated with these unique integers.
Factors in R | How to create a factor in R? - EDUCBA factor(x = character(), levels, labels = levels, ordered = is.ordered(x)) Where, X is a set of categorical data. As we already discussed it should be a string or integers. Levels are set of value which can be taken by X. Levels contains all the unique value available in the column (x). Labels as the name suggest labeling of the data available at X. Quick-R: Value Labels Value Labels To understand value labels in R, you need to understand the data structure factor. You can use the factor function to create your own value labels. # variable v1 is coded 1, 2 or 3 # we want to attach value labels 1=red, 2=blue, 3=green mydata$v1 <- factor (mydata$v1, levels = c (1,2,3), labels = c ("red", "blue", "green")) R Factors and Tables - Emory University R Factors and Tables. One often has to deal with categorical variables in statistics (i.e., variables at the nominal or ordinal level of measurement). In R, these are best dealt with through the use of factors. For example, fertilizers typically have three main ingredients, nitrogen (N), phosphorous (P), and potassium (K). Changing the order of levels of a factor - cookbook-r.com Changing the order of levels of a factor Problem. You want to change the order in which the levels of a factor appear. Solution. Factors in R come in two varieties: ordered and unordered, e.g., {small, medium, large} and {pen, brush, pencil}.For most analyses, it will not matter whether a factor is ordered or unordered.
Factor Levels in R | DataCamp When you first get a data set, you will often notice that it contains factors with specific factor levels. However, sometimes you will want to change the names of these levels for clarity or other reasons. R allows you to do this with the function levels (): levels (factor_vector) <- c ("name1", "name2",...) Powered by Datacamp Workspace Copy code
15.10 Changing the Names of Factor Levels - R Graphics 11.1 Splitting Data into Subplots with Facets. 11.2 Using Facets with Different Axes. 11.3 Changing the Text of Facet Labels. 11.4 Changing the Appearance of Facet Labels and Headers. 12 Using Colors in Plots. 12.1 Setting the Colors of Objects. 12.2 Representing Variables with Colors.
FACTOR in R [CREATE, CHANGE LABELS and CONVERT data] - R CODER Mar 22, 2020 · The factor function. The factor function allows you to create factors in R. In the following block we show the arguments of the function with a summarized description. factor(x = character(), # Input vector data levels, # Input of unique x values (optional) labels = levels, # Output labels for the levels (optional) exclude = NA, # Values to be excluded from levels ordered = is.ordered(x ...
How to Rename Factor Levels in R? - GeeksforGeeks The factor levels can be renamed using the comparison and indexing operators. The existing factor value is compared and then modified by assigning it to a new value. The changes are made to the existing factor vector. The following syntax is followed : Syntax: levels (fac-vec) [levels (fac-vec)==old-val] <- new-val.
Displaying of factor levels and labels in R - Stack Overflow In the conversion to a matrix, your factors are being represented by their numerical coding, not by the character label. All factors are stored as integers where the first level is 1, and the subsequent levels are appropriately numbered. Your best option for remedying it is to avoid storing factors into matrices. - Benjamin Aug 12, 2015 at 16:50
R - Factor (Category, Enumerated Type) | R | Datacadamia - Data and Co A factor is an integer vector where each integer has a label use the str function to see it. Factors are treated specially by modelling functions like lm () and glm () R - Class R - Colon (:) Operator - Sequence generator R - Step Function Model Ggplot - Order Syntax
R: Factors - ETH Z Duplicated values in labels can be used to map different values of x to the same factor level. exclude: a vector of values to be excluded when forming the set of levels. This may be factor with the same level set as x or should be a character. ordered: logical flag to determine if the levels should be regarded as ordered (in the order given). nmax
Factor in R: Categorical Variable & Continuous Variables - Guru99 Categorical variables in R are stored into a factor. Let's check the code below to convert a character variable into a factor variable in R. Characters are not supported in machine learning algorithm, and the only way is to convert a string to an integer. Syntax factor (x = character (), levels, labels = levels, ordered = is.ordered (x)) Arguments:
How to count values per level in a factor in R - GeeksforGeeks Method 1 : Using summary () method. summary () method in base R is a generic function used to produce result summaries of the results of the functions computed based on the class of the argument passed. The summary () function produces an output of the frequencies of the values per level of the given factor column of the data frame in R.
Renaming levels of a factor - cookbook-r.com It's possible to rename factor levels by name (without plyr), but keep in mind that this works only if ALL levels are present in the list; if any are not in the list, they will be replaced with NA. It's also possible to use R's string search-and-replace functions to rename factor levels. Note that the ^ and $ surrounding alpha are there ...
Mathematics | Free Full-Text | Q or R Factor Analysis for Subjectiveness Measurement in Consumer ...
How to Rename Factor Levels in R using levels() and dplyr - Erik Marsja Furthermore, we can see that this variable has two factor levels. In the, we are going to use levels() to change the name of the levels of a categorical variable. First, we are just assigning a character vector with the new names. Second, we are going to use a list renaming the factor levels by name. Example 1: Rename Factor Levels in R with ...
R Factors and Factor Levels (With Examples) - DataMentor Here, we can see that factor x has four elements and two levels. We can check if a variable is a factor or not using class () function. Similarly, levels of a factor can be checked using the levels () function. > class (x) [1] "factor" > levels (x) [1] "married" "single" How to create a factor in R?
Levels in R: What are the Factor Levels - R-Lang Levels of a factor are gathered from the data if not provided. Levels in R The levels () is an inbuilt R function that provides access to the levels attribute. The first form returns the value of the levels of its argument, and the second sets the attribute. You can assign the individual levels using the gl () function.
relabel.factor function - RDocumentation Relabel the levels of factors to provide more descriptive names and reduce the number of factor levels. RDocumentation. Search all packages and functions. BCA (version 0.9-3) Description Usage. Arguments. Value Details. Powered by ...
Getting Started with R - Part 7: Factors - Levels and Labels You can set the levels labels after constructing a factor. This would be similar to passing in the labels parameter. We can pass a full new vector or just labels the labels of the levels selectively. Let us just change factor label 1 from "Jack" to "Mr. Prelutsky". levels(repeat_factor_labeled) [1] <- "Mr. Prelutsky" repeat_factor_labeled
Factor variables | R Learning Modules Factor variables. Version info: Code for this page was tested in R version 3.0.2 (2013-09-25) On: 2013-11-27 With: knitr 1.5 1. Creating factor variables. Factor variables are categorical variables that can be either numeric or string variables. There are a number of advantages to converting categorical variables to factor variables.
gl() Function in R (2 Examples) | How to Generate Factor Levels & Labels As you can see based on the previous output of the RStudio console, we have created a new data object called x1, which contains 15 elements and three different factor levels. Example 2: Specify Labels within gl () Function The following R code illustrates how to change the values (i.e. the labels) of a factor variable created by the gl function.










Post a Comment for "41 r factor levels labels"